Recombinant Human Double-stranded RNA-specific adenosine deaminase (ADAR) , partial
CAT:
399-CSB-EP001324HUe0-01
Size:
1 mg
Price:
Ask
- Availability: 24/48H Stock Items & 2 to 6 Weeks non Stock Items.
- Dry Ice Shipment: No
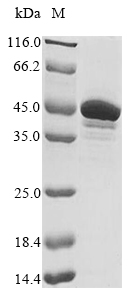



Recombinant Human Double-stranded RNA-specific adenosine deaminase (ADAR) , partial
- CAS Number: 9000-83-3
- Gene Name: ADAR
- UniProt: P55265
- Expression Region: 1-176aa
- Organism: Homo sapiens
- Target Sequence: MNPRQGYSLSGYYTHPFQGYEHRQLRYQQPGPGSSPSSFLLKQIEFLKGQLPEAPVIGKQTPSLPPSLPGLRPRFPVLLASSTRGRQVDIRGVPRGVHLRSQGLQRGFQHPSPRGRSLPQRGVDCLSSHFQELSIYQDQEQRILKFLEELGEGKATTAHDLSGKLGTPKKEINRVL
- Tag: N-terminal GST-tagged
- Source: E.coli
- Field of Research: Epigenetics and Nuclear Signaling
- Assay Type: In Stock Protein
- Relevance: Catalyzes the hydrolytic deamination of adenosine to inosine in double-stranded RNA referred to as A-to-I RNA editing. This may affect gene expression and function in a number of ways that include mRNA translation by changing codons and hence the amino acid sequence of proteins; pre-mRNA splicing by altering splice site recognition sequences; RNA stability by changing sequences involved in nuclease recognition; genetic stability in the case of RNA virus genomes by changing sequences during viral RNA replication; and RNA structure-dependent activities such as microRNA production or targeting or protein-RNA interactions. Can edit both viral and cellular RNAs and can edit RNAs at multiple sites or at specific sites. Its cellular RNA substrates include: bladder cancer-associated protein, neurotransmitter receptors for glutamate and serotonin and GABA receptor. Site-specific RNA editing of transcripts encoding these proteins results in amino acid substitutions which consequently alters their functional activities. Exhibits low-level editing at the GRIA2 Q/R site, but edits efficiently at the R/G site and HOTSPOT1. Its viral RNA substrates include: hepatitis C virus, vesicular stomatitis virus, measles virus, hepatitis delta virus, and human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Exhibits either a proviral or an antiviral effect and this can be editing-dependent, editing-independent or both. Impairs HCV replication via RNA editing at multiple sites. Enhances the replication of MV, VSV and HIV-1 through an editing-independent mechanism via suppression of EIF2AK2/PKR activation and function. Stimulates both the release and infectivity of HIV-1 viral particles by an editing-dependent mechanism where it associates with viral RNAs and edits adenosines in the 5'UTR and the Rev and Tat coding sequence. Can enhance viral replication of HDV via A-to-I editing at a site designated as amber/W, thereby changing an UAG amber stop codon to an UIG tryptophan codon that permits synthesis of the large delta antigen which has a key role in the assembly of viral particles. However, high levels of ADAR1 inhibit HDV replication.
- Purity: Greater than 85% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
- Activity: Not Test
- Length: Partial
- Form: Liquid or Lyophilized powder
- Buffer: If the delivery form is liquid, the default storage buffer is Tris/PBS-based buffer, 5%-50% glycerol. If the delivery form is lyophilized powder, the buffer before lyophilization is Tris/PBS-based buffer, 6% Trehalose, pH 8.0.
- Reconstitution: We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
- Molecular Weight: 47.2 kDa
- References & Citations: "Human RNA-specific adenosine deaminase ADAR1 transcripts possess alternative exon 1 structures that initiate from different promoters, one constitutively active and the other interferon inducible." George C.X., Samuel C.E. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96:4621-4626 (1999)
- Storage Conditions: The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself. Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20℃/-80℃. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20℃/-80℃.
