Acetylated Lysine Antibody: RPE
CAT:
400-SPC-155D-RPE
Size:
100 µg
Price:
Ask
- Availability: 24/48H Stock Items & 2 to 6 Weeks non Stock Items.
- Dry Ice Shipment: No
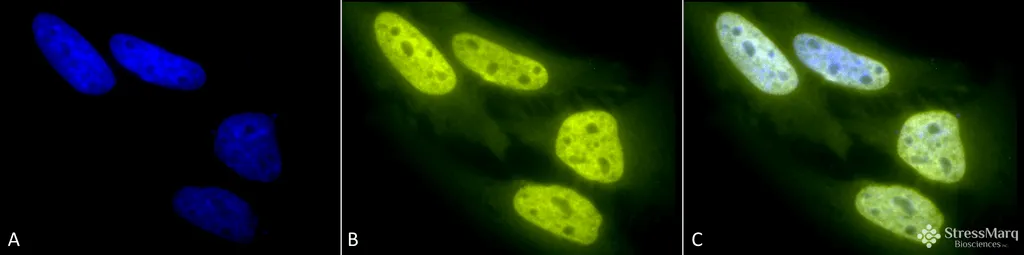
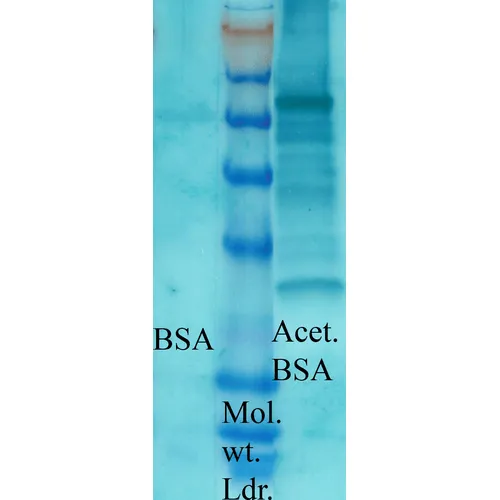
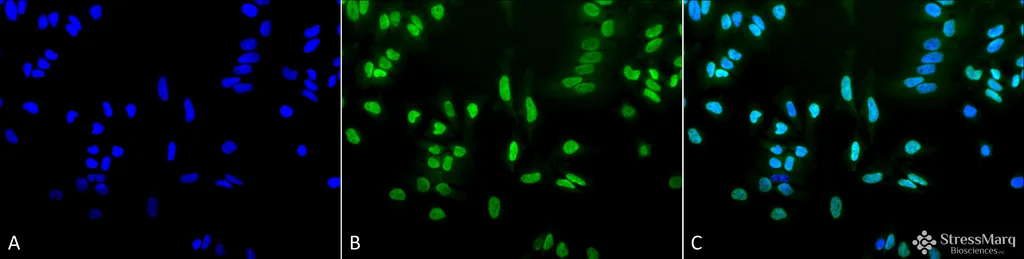
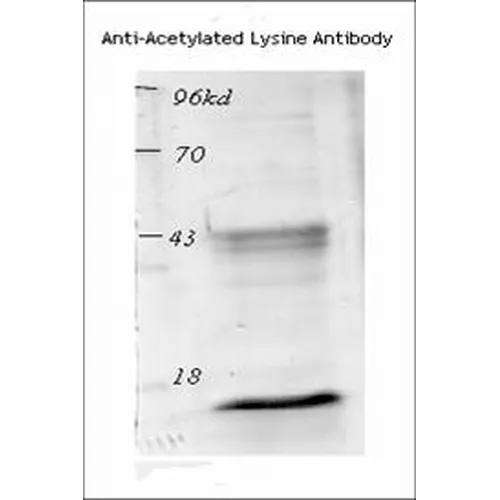






Acetylated Lysine Antibody: RPE
- Background: Post-translational modifications of proteins play critical roles in the regulation and function of many known biological processes. Proteins can be post-translationally modified in many different ways, and a common post-transcriptional modification of Lysine involves acetylation (1). The conserved amino-terminal domains of the four core histones (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4) contain lysines that are acetylated by histone acetyltransferases (HATs) and deacetylated by histone deacetylases (HDACs) (2). Protein posttranslational reversible lysine Nε-acetylation and deacetylation have been recognized as an emerging intracellular signaling mechanism that plays critical roles in regulating gene transcription, cell-cycle progression, apoptosis, DNA repair, and cytoskeletal organization (3). The regulation of protein acetylation status is impaired in the pathologies of cancer and polyglutamine diseases (4), and HDACs have become promising targets for anti-cancer drugs currently in development (5).
- Description: Rabbit Anti-Acetylated Lysine Polyclonal
- Specifications: Detects proteins containing acetylated lysine residues. No reaction to non-acetylated proteins.
- Product Name Alternative: Cell Signaling, Post-translational Modifications, Acetylation
- CAS Number: 9007-83-4
- UNSPSC: 12352203
- Host: Rabbit
- Species Reactivity: Species Independent
- Immunogen: Acetylated KLH Conjugated
- Target: Acetylated Lysine
- Clonality: Polyclonal
- Conjugation: RPE
- Validated Applications: WB, IHC, ICC/IF
- Purification: Protein A Purified
- Concentration: 1 mg/ml
- Dilution: WB (1:250), ICC/IF (1:100); optimal dilutions for assays should be determined by the user.
- Weight: 0.1
- Buffer: 95.64mM Phosphate, 2.48mM MES and 2mM EDTA
- Precautions: Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only.
- References & Citations: 1. Yang X.J. (2005) Oncogene. 24:1653-1662. 2. Hassig C.A. and Schreiber S.L. (1997) Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 1(3): 300-308. 3. Yang X.J. (2004) Bioessays 26:1076-1087. 4. Hughes R.E. (2002) Curr. Biol. 12: R141-R143. 5. Vigushin D.M. and Coombes R.C. (2004) Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 4: 205-218. 6. Chan H.M. et al. (2001) Nat. Cell Biol. 3: 667-674. 7. Martinez-Balbas M.A. et al. (2000) EMBO J. 19: 662-671.
