Filters
Host (770442)
Bovine (1090)Canine (20)Cat (403)Chicken (1642)Cod (2)Cow (333)Crab (15)Dog (524)Dolphin (2)Duck (13)E Coli (239120)Equine (7)Feline (1864)Ferret (306)Fish (125)Frog (52)Goat (36847)Guinea Pig (752)Hamster (1376)Horse (903)Insect (2053)Mammalian (512)Mice (6)Monkey (622)Mouse (96350)Pig (197)Porcine (70)Rabbit (360487)Rat (11703)Ray (55)Salamander (4)Salmon (15)Shark (3)Sheep (4247)Snake (4)Swine (301)Turkey (57)Whale (3)Yeast (5335)Zebrafish (3022)Isotype (157270)
IgA (13685)IgA1 (943)IgA2 (319)IgD (1964)IgE (5630)IgG (87508)IgG1 (16749)IgG2 (1328)IgG3 (2724)IgG4 (1692)IgM (22194)IgY (2534)Label (235733)
AF488 (2465)AF594 (662)AF647 (2324)ALEXA (11545)ALEXA FLUOR 350 (255)ALEXA FLUOR 405 (260)ALEXA FLUOR 488 (672)ALEXA FLUOR 532 (260)ALEXA FLUOR 555 (274)ALEXA FLUOR 568 (253)ALEXA FLUOR 594 (299)ALEXA FLUOR 633 (262)ALEXA FLUOR 647 (607)ALEXA FLUOR 660 (252)ALEXA FLUOR 680 (422)ALEXA FLUOR 700 (2)ALEXA FLUOR 750 (414)ALEXA FLUOR 790 (215)Alkaline Phosphatase (825)Allophycocyanin (32)ALP (387)AMCA (80)AP (1159)APC (14233)APC C750 (13)Apc Cy7 (1248)ATTO 390 (3)ATTO 488 (6)ATTO 550 (1)ATTO 594 (5)ATTO 647N (4)AVI (53)Beads (235)Beta Gal (2)BgG (1)BIMA (6)Biotin (27817)Biotinylated (1810)Blue (708)BSA (878)BTG (46)C Terminal (688)CF Blue (19)Colloidal (22)Conjugated (29281)Cy (163)Cy3 (390)Cy5 (2041)Cy5 5 (2469)Cy5 PE (1)Cy7 (3638)Dual (170)DY549 (3)DY649 (3)Dye (1)DyLight (1430)DyLight 405 (7)DyLight 488 (216)DyLight 549 (17)DyLight 594 (84)DyLight 649 (3)DyLight 650 (35)DyLight 680 (17)DyLight 800 (21)Fam (13)Fc Tag (8)FITC (29181)Flag (208)Fluorescent (146)GFP (576)GFP Tag (180)Glucose Oxidase (59)Gold (511)Green (580)GST (722)GST Tag (327)HA Tag (440)His (634)His Tag (507)Horseradish (550)HRP (12994)HSA (247)iFluor (16571)Isoform b (31)KLH (87)Luciferase (105)Magnetic (260)MBP (343)MBP Tag (93)Myc Tag (410)OC 515 (1)Orange (78)OVA (103)Pacific Blue (213)Particle (64)PE (32633)PerCP (7450)Peroxidase (1364)POD (11)Poly Hrp (94)Poly Hrp40 (13)Poly Hrp80 (3)Puro (32)Red (2440)RFP Tag (63)Rhodamine (607)RPE (910)S Tag (194)SCF (184)SPRD (351)Streptavidin (55)SureLight (77)T7 Tag (97)Tag (4806)Texas (1249)Texas Red (1231)Triple (10)TRITC (1401)TRX tag (90)Unconjugated (2110)Unlabeled (218)Yellow (84)Pathogen (489480)
Adenovirus (8685)AIV (317)Bordetella (25032)Borrelia (18284)Candida (17811)Chikungunya (638)Chlamydia (17663)CMV (121402)Coronavirus (5949)Coxsackie (859)Dengue (2872)EBV (1497)Echovirus (215)Enterovirus (677)Hantavirus (259)HAV (909)HBV (2084)HHV (838)HIV (7876)hMPV (275)HSV (2334)HTLV (635)Influenza (22004)Isolate (1208)KSHV (396)Lentivirus (3755)Lineage (3025)Lysate (127759)Marek (94)Measles (1169)Parainfluenza (1692)Poliovirus (3024)Poxvirus (81)Rabies (1526)Reovirus (536)Retrovirus (1066)Rhinovirus (511)Rotavirus (5353)RSV (1768)Rubella (1070)SIV (279)Strain (67791)Vaccinia (7232)VZV (661)WNV (369)Species (2980604)
Alligator (10)Bovine (159815)Canine (120805)Cat (13115)Chicken (113989)Cod (1)Cow (2031)Dog (12723)Dolphin (21)Duck (9606)Equine (2012)Feline (1019)Ferret (259)Fish (12882)Frog (1)Goat (90541)Guinea Pig (87960)Hamster (36960)Horse (41294)Human (950231)Insect (653)Lemur (119)Lizard (24)Monkey (110994)Mouse (470765)Pig (26229)Porcine (131969)Rabbit (127889)Rat (349272)Ray (443)Salmon (348)Seal (8)Shark (29)Sheep (105155)Snake (11)Swine (519)Toad (4)Turkey (244)Turtle (75)Whale (45)Zebrafish (534)Technique (5589781)
Activation (170412)Activity (10795)Affinity (44634)Agarose (2604)Aggregation (199)Antigen (135460)Apoptosis (27407)Array (2022)Blocking (71768)Blood (8530)Blot (10966)ChiP (814)Chromatin (6286)Colorimetric (9907)Control (80079)Culture (3219)Cytometry (5475)Depletion (56)DNA (172527)Dot (233)EIA (1039)Electron (6275)Electrophoresis (254)Elispot (1294)Enzymes (52765)Exosome (4280)Extract (1090)Fab (2227)FACS (43)FC (80717)Flow (6662)Fluorometric (1406)Formalin (97)Frozen (2671)Functional (708)Gel (2480)HTS (136)IF (12906)IHC (16566)Immunoassay (1589)Immunofluorescence (4119)Immunohistochemistry (72)Immunoprecipitation (68)intracellular (5602)IP (2838)iPSC (259)Isotype (8804)Lateral (1587)Lenti (319416)Light (37303)Microarray (47)MicroRNA (4835)Microscopy (52)miRNA (88042)Monoclonal (524801)Multi (3844)Multiplex (302)Negative (4261)PAGE (2521)Panel (1633)Paraffin (2587)PBS (20266)PCR (9)Peptide (276278)PerCP (12769)Polyclonal (2747043)Positive (6336)Precipitation (61)Premix (130)Primers (3467)Probe (2630)Profile (229)Pure (7818)Purification (15)Purified (78235)Real Time (3042)Resin (2975)Reverse (2438)RIA (460)RNAi (17)Rox (1023)RT PCR (6608)Sample (2666)SDS (1524)Section (2895)Separation (86)Sequencing (122)Shift (22)siRNA (319447)Standard (42465)Sterile (10168)Strip (1863)Taq (2)Tip (1172)Tissue (42847)Tube (3306)Vitro (3577)Vivo (981)WB (2515)Western Blot (10683)Tissue (2017019)
Adenocarcinoma (1075)Adipose (3463)Adrenal (657)Adult (4883)Amniotic (65)Animal (2452)Aorta (436)Appendix (89)Array (2022)Ascites (4737)Bile Duct (20)Bladder (1675)Blood (8530)Bone (27367)Brain (31217)Breast (10918)Calvaria (28)Carcinoma (13497)cDNA (58548)Cell (413914)Cellular (9360)Cerebellum (700)Cervix (232)Child (1)Choroid (19)Colon (3911)Connective (3603)Contaminant (3)Control (80079)Cord (661)Corpus (148)Cortex (698)Dendritic (1849)Diseased (265)Donor (1360)Duct (861)Duodenum (643)Embryo (425)Embryonic (4586)Endometrium (466)Endothelium (1424)Epidermis (166)Epithelium (4224)Esophagus (716)Exosome (4280)Eye (2033)Female (475)Frozen (2671)Gallbladder (155)Genital (5)Gland (3437)Granulocyte (8990)Heart (6851)Hela (413)Hippocampus (325)Histiocytic (74)Ileum (201)Insect (4880)Intestine (1945)Isolate (1208)Jejunum (175)Kidney (8079)Langerhans (283)Leukemia (21573)Liver (17342)Lobe (835)Lung (6074)Lymph (1208)Lymphatic (639)lymphocyte (22589)Lymphoma (12787)Lysate (127759)Lysosome (2814)Macrophage (31832)Male (1617)Malignant (1467)Mammary (1987)Mantle (1042)Marrow (2210)Mastocytoma (3)Matched (11710)Medulla (156)Melanoma (15525)Membrane (105780)Metastatic (3575)Mitochondrial (160331)Muscle (37428)Myeloma (748)Myocardium (11)Nerve (6403)Neuronal (17035)Node (1206)Normal (9488)Omentum (10)Ovarian (2511)Ovary (1173)Pair (47185)Pancreas (2843)Panel (1633)Penis (64)Peripheral (1912)Pharynx (122)Pituitary (5421)Placenta (4051)Prostate (9438)Proximal (318)Rectum (316)Region (202208)Retina (956)Salivary (3119)Sarcoma (6946)Section (2895)Serum (24921)Set (167648)Skeletal (13636)Skin (1882)Smooth (7575)Spinal (424)Spleen (2292)Stem (8901)Stomach (925)Stroma (49)Subcutaneous (47)Testis (15396)Thalamus (127)Thoracic (60)Throat (40)Thymus (2988)Thyroid (14138)Tongue (144)Total (10151)Trachea (227)Transformed (175)Tubule (48)Tumor (76992)Umbilical (208)Ureter (73)Urinary (2467)Uterine (303)Uterus (414)Non-Coding RNA & Neuroinflammation in MDD | Molecular Mechanisms & circRNA Biomarkers
Explore the role of non-coding RNAs including circRNAs like circDYM, circHIPK2, and circSTAG1 in neuroinflammatory pathways linked to Major Depressive Disorder (MDD), with implications for RT-PCR-based diagnostics and targeted therapy development.
Gentaur
Scientific Publications
Non-Coding RNA & Neuroinflammation in MDD | Molecular Mechanisms & circRNA Biomarkers
Molecular Regulation of Neuroinflammation in MDD via Non-Coding RNAs
Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) is increasingly recognized as a multifactorial disorder involving dysregulation of neuroinflammatory signaling , glial activation , and non-coding RNA (ncRNA)-mediated gene expression . Recent studies published in International Journal of Biological Macromolecules (2024) , Journal of Extracellular Vesicles (2022) , Molecular Psychiatry (2020) , and Biological Psychiatry (2020) have provided mechanistic insights into how circular RNAs (circRNAs) modulate microglial and astrocytic function through miRNA sponging, epigenetic regulation, and extracellular vesicle (EV)-mediated intercellular communication.
This article delves into :
- The functional roles of specific circRNAs—circDYM , circHIPK2 , circSTAG1
- Their interactions with miRNAs such as miR-9 , miR-16-5p , and miR-34a
- Neuroinflammatory pathways regulated by NLRP3 inflammasome , m6A methylation , and astrocyte dysfunction
- Applications in RT-PCR detection kits and precision psychiatry
circDYM Expression Is Downregulated in LPS-Induced Depression Models
In Molecular Psychiatry (2020) , it was demonstrated that circDYM levels are significantly reduced in both chronic unpredictable stress (CUS) mouse models and LPS-treated BV2 microglial cells . Lentiviral overexpression of circDYM attenuated LPS-induced LC3B-II accumulation and cleaved caspase-3 expression , indicating a protective effect against neuroinflammation and apoptosis.
Mechanistically, circDYM functions as a miR-9 sponge , preventing miR-9-mediated suppression of HECT domain-containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1 (HECTD1) . HECTD1 stabilizes HSP90 ubiquitination , thereby reducing microglial activation and neuroinflammatory cytokine release.
These findings suggest that circDYM downregulation contributes to glial hyperactivation in depression, and its restoration may serve as a therapeutic strategy.

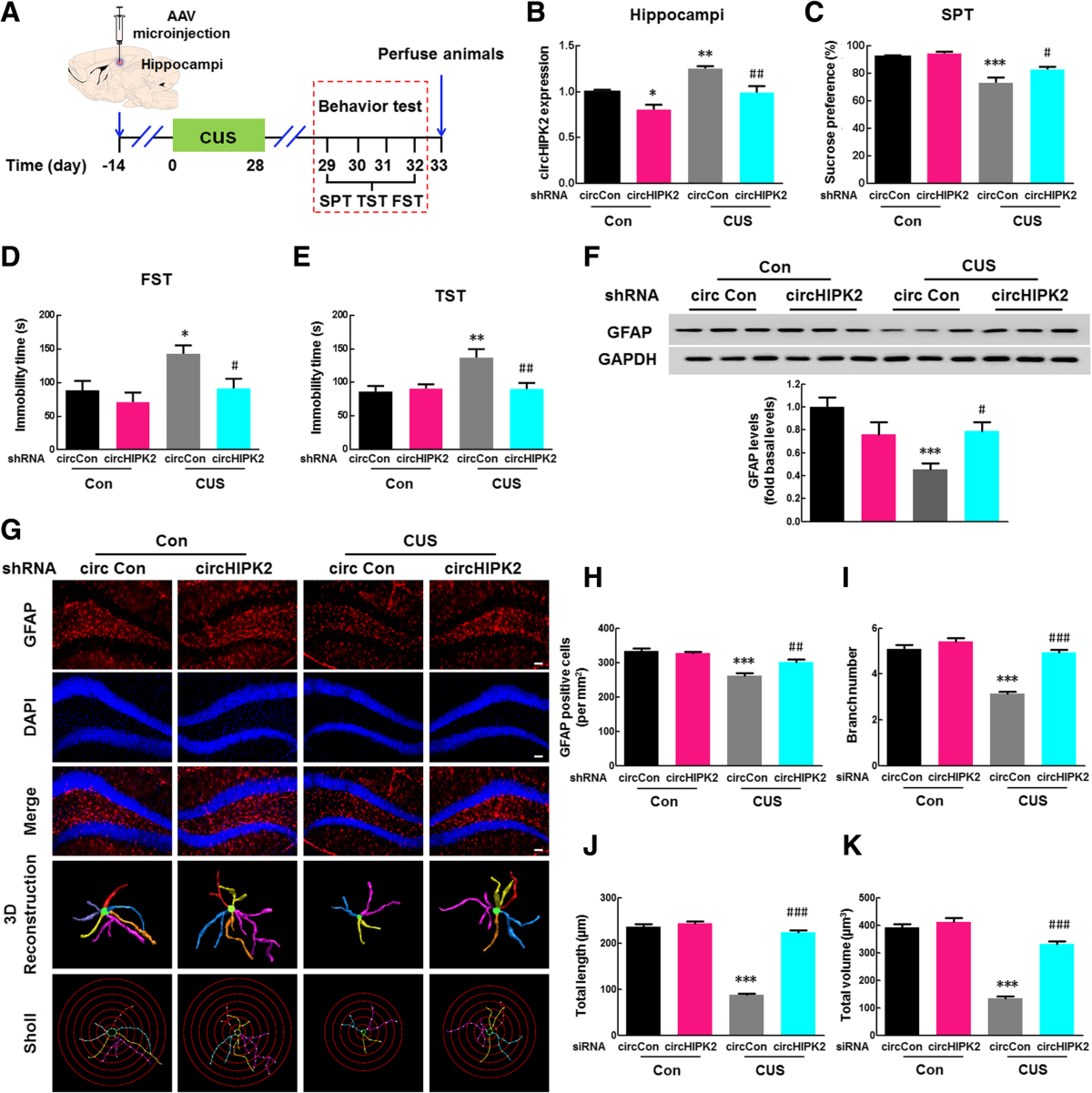
NLRP3 Deficiency Alters circHIPK2 Levels via Fecal Microbiota Transplantation (FMT)
The Microbiome (2019) study revealed that circHIPK2 expression in the hippocampus and plasma is elevated following CUS exposure in wild-type (WT) microbiota recipient mice. However, transplantation of NLRP3 knockout (KO) microbiota significantly suppressed circHIPK2 upregulation and alleviated depressive-like behaviors.
Using GFP-labeled lentivirus microinjection , the authors showed that circHIPK2 knockdown in astrocytes mimicked the antidepressant effects observed in NLRP3 KO microbiota recipients.
These data support a model where circHIPK2 mediates astrocytic dysfunction downstream of gut-derived inflammatory signals , positioning it as a gut-brain axis-linked biomarker in MDD.
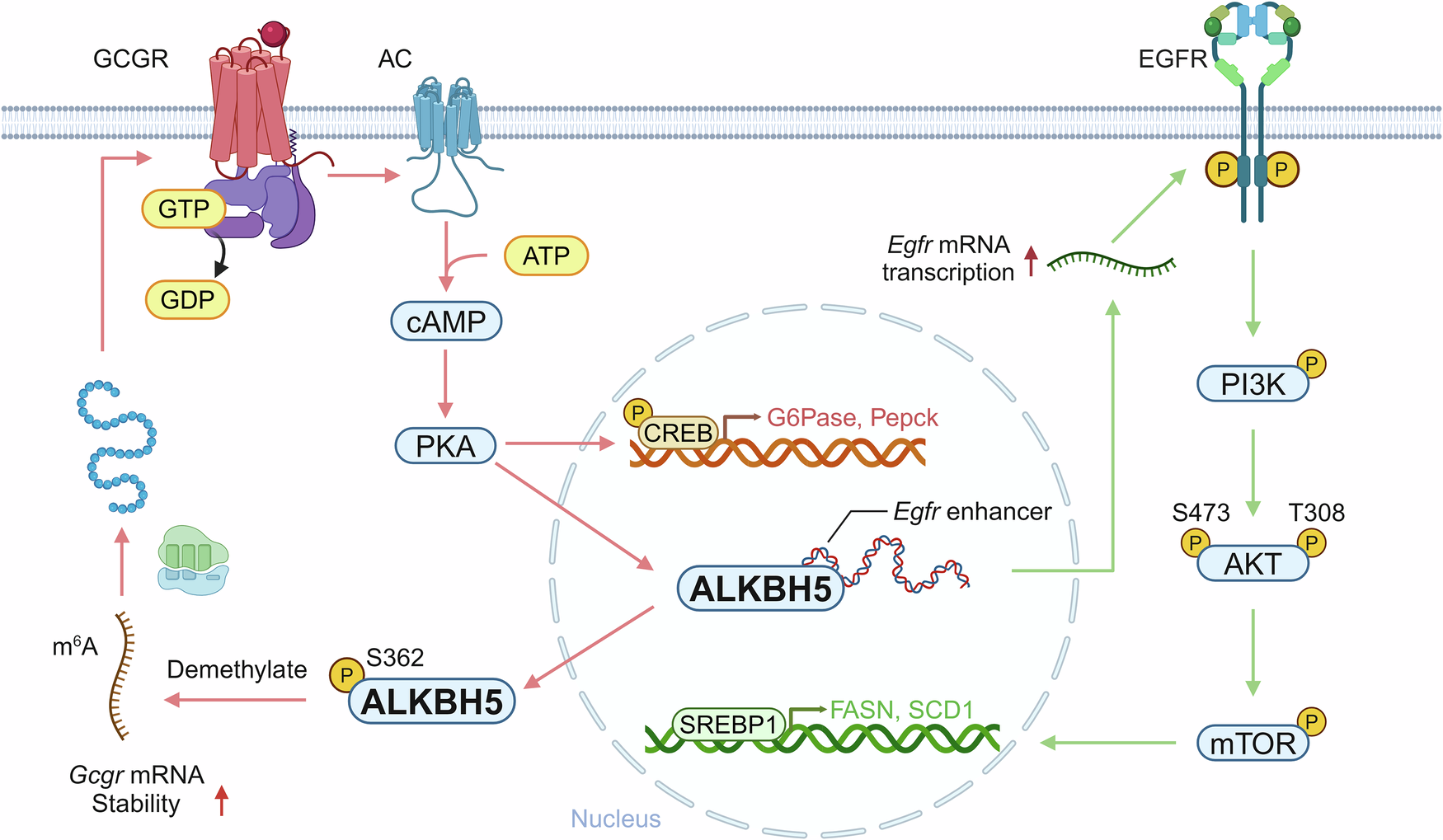
circSTAG1 Regulates ALKBH5-FAAH Signaling Pathway
According to Biological Psychiatry (2020) , circSTAG1 is downregulated in MDD patients and correlates with symptom severity. circSTAG1 interacts with ALKBH5 , an m6A demethylase, and modulates FAAH expression—a key enzyme in endocannabinoid metabolism.
This interaction affects m6A RNA methylation status , which in turn influences astrocyte transcriptomic profiles and synaptic plasticity .
Notably, circSTAG1 loss leads to increased m6A methylation at FAAH mRNA , enhancing its stability and contributing to endocannabinoid system dysregulation —a known feature of depression pathophysiology.
circ_0000831/miR-16-5p Axis in Inflammatory Response
The Int J Biol Macromol (2024) paper reported that circ_0000831 exhibits anti-inflammatory properties in cerebral ischemia models by acting as a miR-16-5p sponge . Overexpression of circ_0000831 reduced TNF-α , IL-6 , and IL-1β levels in BV2 microglial cells treated with LPS.
While this study focused on vertigo and stroke, the conserved miR-16-5p binding motif suggests potential relevance in MDD-associated neuroinflammation , particularly in comorbid conditions involving vascular pathology or chronic inflammation.
RVG-EVs Deliver circDYM to Microglia with High Efficiency
The J Extracell Vesicles (2022) study described the use of rabies virus glycoprotein (RVG)-modified EVs to deliver circDYM-GFP into the central nervous system (CNS).
Engineered EVs were isolated from HEK293T cells transfected with RVG-Lamp2b plasmid and circDYM-GFP lentivirus , then purified using Exo-spin™ SEC columns .
These EVs efficiently delivered circDYM to primary mouse microglia , as confirmed by absolute qPCR and fluorescence imaging . The delivery resulted in significant reductions in LPS-induced pro-inflammatory cytokines , demonstrating the feasibility of circRNA-based EV therapeutics in neuroinflammatory disorders.

PCR, Western Blot, and Immunofluorescence in circRNA Studies
Across these studies, the following techniques were used to validate circRNA function:
- Quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) using divergent primers to detect back-spliced junctions
- Western blotting to assess protein expression of HECTD1, HSP90, LC3B, cleaved caspase-3
- Immunofluorescence staining with GFAP (astrocytes), IBA1 (microglia), NeuN (neurons)
- Behavioral assays : Sucrose preference test (SPT), tail suspension test (TST), forced swim test (FST)
These methods provide a robust framework for studying circRNA dynamics in vivo and in vitro .
From ncRNA Discovery to Precision Psychiatry
The integration of non-coding RNA biology , neuroinflammatory signaling , and extracellular vesicle engineering offers a transformative approach to understanding and treating Major Depressive Disorder . circRNAs such as circDYM , circHIPK2 , circSTAG1 , and circ_0000831 represent promising diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets , particularly when analyzed using RT-PCR detection kits and validated via behavioral and biochemical assays .
As our understanding of these molecular mechanisms deepens, so too does the potential for personalized treatment strategies based on individual circRNA profiles, paving the way toward precision psychiatry .