Filters
Host (768769)
Bovine (1090)Canine (20)Cat (408)Chicken (1657)Cod (2)Cow (333)Crab (15)Dog (524)Dolphin (2)Duck (13)E Coli (239129)Equine (7)Feline (1864)Ferret (306)Fish (125)Frog (55)Goat (36948)Guinea Pig (752)Hamster (1376)Horse (903)Insect (2053)Mammalian (512)Mice (6)Monkey (601)Mouse (96266)Pig (197)Porcine (70)Rabbit (358746)Rat (11724)Ray (55)Salamander (4)Salmon (15)Shark (3)Sheep (4265)Snake (4)Swine (301)Turkey (57)Whale (3)Yeast (5336)Zebrafish (3022)Isotype (156829)
IgA (13613)IgA1 (939)IgA2 (317)IgD (1946)IgE (5582)IgG (87389)IgG1 (16732)IgG2 (1331)IgG3 (2717)IgG4 (1687)IgM (22026)IgY (2550)Label (239355)
AF488 (2465)AF594 (662)AF647 (2324)ALEXA (11546)ALEXA FLUOR 350 (255)ALEXA FLUOR 405 (260)ALEXA FLUOR 488 (672)ALEXA FLUOR 532 (260)ALEXA FLUOR 555 (274)ALEXA FLUOR 568 (253)ALEXA FLUOR 594 (299)ALEXA FLUOR 633 (262)ALEXA FLUOR 647 (607)ALEXA FLUOR 660 (252)ALEXA FLUOR 680 (422)ALEXA FLUOR 700 (2)ALEXA FLUOR 750 (414)ALEXA FLUOR 790 (215)Alkaline Phosphatase (825)Allophycocyanin (32)ALP (387)AMCA (80)AP (1160)APC (15217)APC C750 (13)Apc Cy7 (1248)ATTO 390 (3)ATTO 488 (6)ATTO 550 (1)ATTO 594 (5)ATTO 647N (4)AVI (53)Beads (225)Beta Gal (2)BgG (1)BIMA (6)Biotin (27821)Biotinylated (1810)Blue (708)BSA (878)BTG (46)C Terminal (688)CF Blue (19)Colloidal (22)Conjugated (29246)Cy (163)Cy3 (390)Cy5 (2041)Cy5 5 (2469)Cy5 PE (1)Cy7 (3638)Dual (170)DY549 (3)DY649 (3)Dye (1)DyLight (1430)DyLight 405 (7)DyLight 488 (216)DyLight 549 (17)DyLight 594 (84)DyLight 649 (3)DyLight 650 (35)DyLight 680 (17)DyLight 800 (21)Fam (5)Fc Tag (8)FITC (30172)Flag (208)Fluorescent (146)GFP (563)GFP Tag (164)Glucose Oxidase (59)Gold (511)Green (580)GST (711)GST Tag (315)HA Tag (430)His (619)His Tag (492)Horseradish (550)HRP (12964)HSA (249)iFluor (16571)Isoform b (31)KLH (88)Luciferase (105)Magnetic (254)MBP (338)MBP Tag (87)Myc Tag (398)OC 515 (1)Orange (78)OVA (104)Pacific Blue (213)Particle (64)PE (33571)PerCP (8438)Peroxidase (1380)POD (11)Poly Hrp (92)Poly Hrp40 (13)Poly Hrp80 (3)Puro (32)Red (2440)RFP Tag (63)Rhodamine (607)RPE (910)S Tag (194)SCF (184)SPRD (351)Streptavidin (55)SureLight (77)T7 Tag (97)Tag (4710)Texas (1249)Texas Red (1231)Triple (10)TRITC (1401)TRX tag (87)Unconjugated (2110)Unlabeled (218)Yellow (84)Pathogen (489908)
Adenovirus (8660)AIV (315)Bordetella (25035)Borrelia (18281)Candida (17817)Chikungunya (638)Chlamydia (17650)CMV (121394)Coronavirus (5948)Coxsackie (852)Dengue (2867)EBV (1510)Echovirus (215)Enterovirus (677)Hantavirus (254)HAV (903)HBV (2095)HHV (873)HIV (7865)hMPV (300)HSV (2356)HTLV (634)Influenza (22132)Isolate (1208)KSHV (396)Lentivirus (3755)Lineage (3022)Lysate (127759)Marek (93)Measles (1163)Parainfluenza (1681)Poliovirus (3027)Poxvirus (74)Rabies (1519)Reovirus (527)Retrovirus (1069)Rhinovirus (507)Rotavirus (5346)RSV (1781)Rubella (1070)SIV (277)Strain (68102)Vaccinia (7232)VZV (666)WNV (363)Species (2973193)
Alligator (10)Bovine (159561)Canine (120646)Cat (13069)Chicken (113597)Cod (1)Cow (2030)Dog (12544)Dolphin (21)Duck (9565)Equine (2004)Feline (996)Ferret (259)Fish (12797)Frog (1)Goat (90404)Guinea Pig (87845)Hamster (36935)Horse (41101)Human (950923)Insect (653)Lemur (118)Lizard (24)Monkey (110914)Mouse (468899)Pig (25918)Porcine (131703)Rabbit (127434)Rat (346119)Ray (437)Salmon (347)Seal (8)Shark (29)Sheep (104910)Snake (12)Swine (511)Toad (4)Turkey (244)Turtle (75)Whale (45)Zebrafish (480)Technique (5600522)
Activation (170361)Activity (10723)Affinity (44699)Agarose (2604)Aggregation (199)Antigen (135262)Apoptosis (27422)Array (2022)Blocking (71767)Blood (9449)Blot (10966)ChiP (814)Chromatin (6283)Colorimetric (9913)Control (82142)Culture (3226)Cytometry (5481)Depletion (54)DNA (172411)Dot (233)EIA (1039)Electron (6272)Electrophoresis (254)Elispot (1294)Enzymes (52648)Exosome (4278)Extract (1090)Fab (2236)FACS (43)FC (80935)Flow (6666)Fluorometric (1407)Formalin (97)Frozen (2678)Functional (708)Gel (2484)HTS (136)IF (12906)IHC (16566)Immunoassay (1589)Immunofluorescence (4119)Immunohistochemistry (72)Immunoprecipitation (68)intracellular (5599)IP (2840)iPSC (259)Isotype (8791)Lateral (1585)Lenti (319416)Light (37225)Microarray (47)MicroRNA (4834)Microscopy (52)miRNA (88043)Monoclonal (516119)Multi (3844)Multiplex (302)Negative (4261)PAGE (2520)Panel (1520)Paraffin (2587)PBS (20270)PCR (9)Peptide (276037)PerCP (13759)Polyclonal (2763048)Positive (6335)Precipitation (61)Premix (130)Primers (3467)Probe (2627)Profile (229)Pure (7808)Purification (15)Purified (78469)Real Time (3042)Resin (2955)Reverse (2432)RIA (460)RNAi (17)Rox (1022)RT PCR (6608)Sample (2667)SDS (1527)Section (2895)Separation (86)Sequencing (122)Shift (22)siRNA (319447)Standard (42483)Sterile (10169)Strip (1863)Taq (2)Tip (1176)Tissue (42741)Tube (3306)Vitro (3577)Vivo (981)WB (2515)Western Blot (10683)Tissue (2020582)
Adenocarcinoma (1075)Adipose (3453)Adrenal (657)Adult (4877)Amniotic (65)Animal (2447)Aorta (436)Appendix (89)Array (2022)Ascites (4377)Bile Duct (20)Bladder (1671)Blood (9449)Bone (27276)Brain (31131)Breast (10905)Calvaria (28)Carcinoma (13486)cDNA (58547)Cell (413637)Cellular (9350)Cerebellum (700)Cervix (232)Child (1)Choroid (19)Colon (3909)Connective (3596)Contaminant (3)Control (82142)Cord (661)Corpus (148)Cortex (698)Dendritic (1849)Diseased (265)Donor (3069)Duct (859)Duodenum (643)Embryo (425)Embryonic (4579)Endometrium (463)Endothelium (1417)Epidermis (166)Epithelium (4212)Esophagus (716)Exosome (4278)Eye (2033)Female (793)Frozen (2678)Gallbladder (155)Genital (5)Gland (3432)Granulocyte (8970)Heart (6843)Hela (413)Hippocampus (325)Histiocytic (74)Ileum (201)Insect (4880)Intestine (1944)Isolate (1208)Jejunum (175)Kidney (8064)Langerhans (283)Leukemia (21520)Liver (17310)Lobe (834)Lung (6058)Lymph (1208)Lymphatic (637)lymphocyte (22550)Lymphoma (12770)Lysate (127759)Lysosome (2812)Macrophage (31747)Male (1935)Malignant (1463)Mammary (1984)Mantle (1042)Marrow (2208)Mastocytoma (3)Matched (11710)Medulla (156)Melanoma (15509)Membrane (105739)Metastatic (3573)Mitochondrial (160265)Muscle (37365)Myeloma (752)Myocardium (11)Nerve (6379)Neuronal (17007)Node (1206)Normal (9486)Omentum (10)Ovarian (2507)Ovary (1172)Pair (47185)Pancreas (2840)Panel (1520)Penis (64)Peripheral (1909)Pharynx (122)Pituitary (5407)Placenta (4032)Prostate (9418)Proximal (318)Rectum (316)Region (202193)Retina (956)Salivary (3113)Sarcoma (6941)Section (2895)Serum (25142)Set (167651)Skeletal (13603)Skin (1878)Smooth (7568)Spinal (424)Spleen (2290)Stem (8883)Stomach (925)Stroma (49)Subcutaneous (47)Testis (15388)Thalamus (127)Thoracic (60)Throat (40)Thymus (2985)Thyroid (14095)Tongue (140)Total (10121)Trachea (227)Transformed (175)Tubule (48)Tumor (76813)Umbilical (208)Ureter (73)Urinary (2465)Uterine (303)Uterus (414)Human Transforming Growth Factor Beta 3 (TGF-β3) Protein : Function, Applications, and Importance in Research
Human Transforming Growth Factor Beta 3 (TGF-β3) is a pivotal protein that plays a crucial role in cellular regulation, tissue development, and immune response modulation. TGF-β3, as part of the TGF-β family, is involved in a variety of biological processes including wound healing, fibrosis, and embryogenesis. This article delves into the significance of TGF-β3 protein, its functions, applications in research, and its potential as a therapeutic target.
Gentaur
Scientific Publications
Human Transforming Growth Factor Beta 3 (TGF-β3) Protein : Function, Applications, and Importance in Research
What is TGF-β3 Protein ?
Transforming Growth Factor Beta 3 (TGF-β3) is one of three isoforms of the TGF-β family, alongside TGF-β1 and TGF-β2. TGF-β3 is essential for cellular differentiation, extracellular matrix formation, and tissue remodeling. The protein is synthesized as a latent precursor and must undergo activation to exert its biological effects, which include regulating immune system responses, cellular growth, and apoptosis.
TGF-β3 Protein Structure and Function
TGF-β3 is a homodimeric protein composed of two identical polypeptide chains held together by disulfide bonds. It binds to TGF-β receptors on the cell surface, activating intracellular signaling pathways that regulate gene expression. These signals are crucial in regulating processes such as cell migration, proliferation, and differentiation.
The Role of TGF-β3 in Development and Wound Healing
TGF-β3 is a key player in embryonic development and wound healing. During tissue repair, TGF-β3 promotes collagen synthesis and helps in the regeneration of epithelial tissues. It has been shown to play a more significant role in scarless wound healing compared to TGF-β1, which typically results in fibrosis and scarring.

TGF-β3 in Embryogenesis
In the early stages of development, TGF-β3 is critical for the formation of ectodermal tissues and mesodermal patterning. The protein regulates the development of tissues such as the skin, cartilage, and neural tissues.
TGF-β3 Protein in Disease and Therapy
The dysregulation of TGF-β3 signaling can lead to various pathological conditions, including fibrosis, cancer, and autoimmune diseases. For example, overexpression of TGF-β3 is often associated with the development of pulmonary fibrosis and scleroderma. Conversely, the inhibition of TGF-β3 signaling could have therapeutic potential in cancer immunotherapy by enabling better immune system responses against tumors.
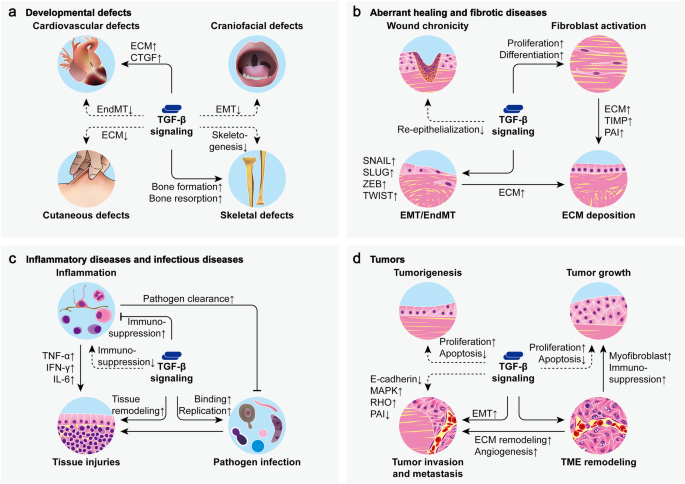
TGF-β3 as a Therapeutic Target
Recent research has focused on modulating TGF-β3 levels for therapeutic purposes. For example, TGF-β3 inhibitors are being investigated as a means to prevent excessive fibrosis and improve wound healing outcomes. Similarly, TGF-β3 activators may enhance tissue regeneration in cases of severe tissue damage or chronic wounds.
TGF-β3 Protein Applications in Research
The use of recombinant TGF-β3 in research has been instrumental in studying various biological processes. Here are some of the key research applications :
- Cell Culture Studies: TGF-β3 is used to study cellular responses such as differentiation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), which is critical in cancer metastasis. Learn more
- Wound Healing Models: TGF-β3 has been applied in in vitro and in vivo models to understand the mechanisms of scarless healing and tissue regeneration.

- Fibrosis Research: As a key regulator of extracellular matrix production, TGF-β3 is used in models investigating fibrosis in organs like the lungs and kidneys.
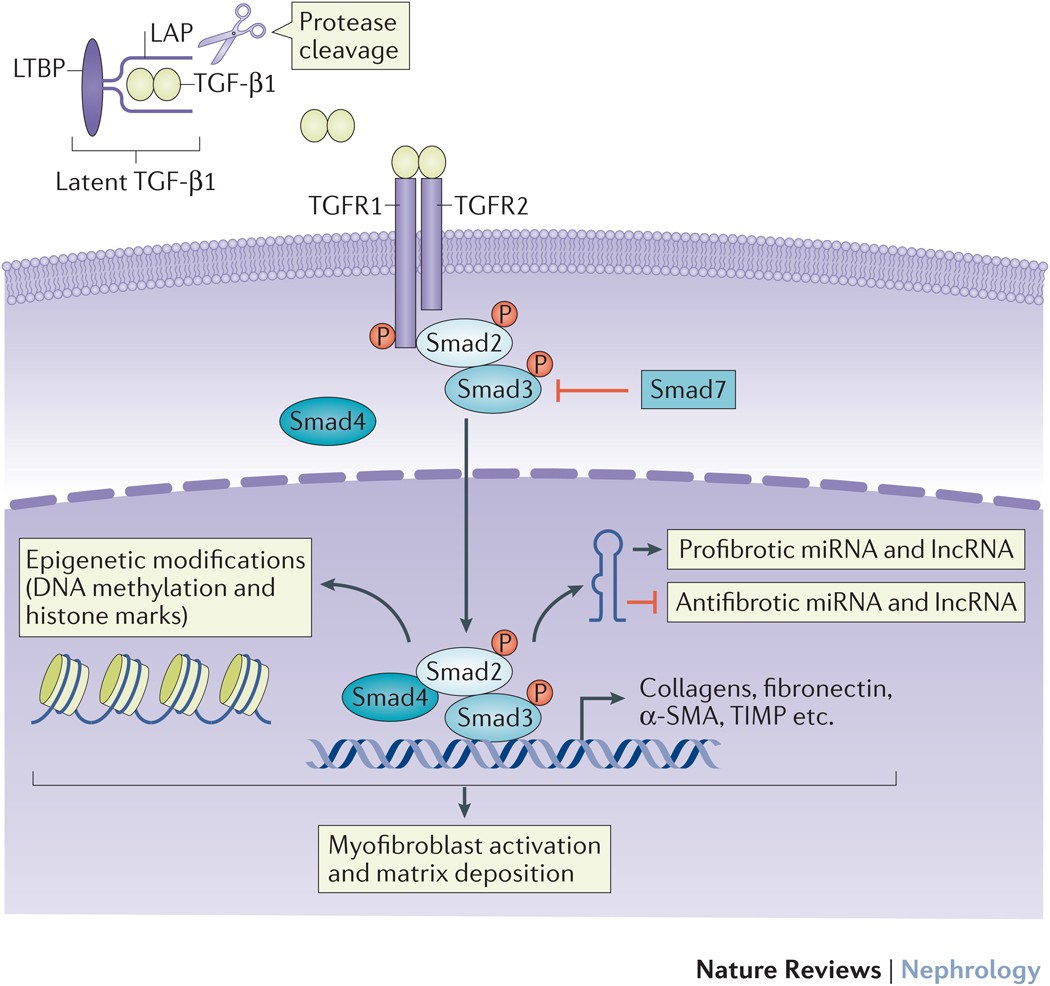
How to Use TGF-β3 Protein in Laboratory Experiments ?
Researchers typically use recombinant TGF-β3 proteins for studying its biological effects. Commercially available TGF-β3 protein preparations are used in cell culture and protein assays to monitor the protein’s impact on cellular functions such as migration, differentiation, and gene expression.
For in vitro studies, TGF-β3 protein can be added to cell culture media to investigate the effects on cell growth and the induction of fibrosis or scar tissue formation.
The Future of TGF-β3 Protein in Therapeutics and Research !
Transforming Growth Factor Beta 3 (TGF-β3) protein is essential for normal cellular functions and development. By understanding its role in tissue remodeling and disease processes, researchers are uncovering new therapeutic strategies for diseases such as fibrosis, cancer, and wound healing. The potential to modulate TGF-β3 levels could lead to improved treatments for these conditions, making it an important target in biomedical research.