Host (770442)
Bovine (1090)Canine (20)Cat (403)Chicken (1642)Cod (2)Cow (333)Crab (15)Dog (524)Dolphin (2)Duck (13)E Coli (239120)Equine (7)Feline (1864)Ferret (306)Fish (125)Frog (52)Goat (36847)Guinea Pig (752)Hamster (1376)Horse (903)Insect (2053)Mammalian (512)Mice (6)Monkey (622)Mouse (96350)Pig (197)Porcine (70)Rabbit (360487)Rat (11703)Ray (55)Salamander (4)Salmon (15)Shark (3)Sheep (4247)Snake (4)Swine (301)Turkey (57)Whale (3)Yeast (5335)Zebrafish (3022)Isotype (157270)
IgA (13685)IgA1 (943)IgA2 (319)IgD (1964)IgE (5630)IgG (87508)IgG1 (16749)IgG2 (1328)IgG3 (2724)IgG4 (1692)IgM (22194)IgY (2534)Label (235733)
AF488 (2465)AF594 (662)AF647 (2324)ALEXA (11545)ALEXA FLUOR 350 (255)ALEXA FLUOR 405 (260)ALEXA FLUOR 488 (672)ALEXA FLUOR 532 (260)ALEXA FLUOR 555 (274)ALEXA FLUOR 568 (253)ALEXA FLUOR 594 (299)ALEXA FLUOR 633 (262)ALEXA FLUOR 647 (607)ALEXA FLUOR 660 (252)ALEXA FLUOR 680 (422)ALEXA FLUOR 700 (2)ALEXA FLUOR 750 (414)ALEXA FLUOR 790 (215)Alkaline Phosphatase (825)Allophycocyanin (32)ALP (387)AMCA (80)AP (1159)APC (14233)APC C750 (13)Apc Cy7 (1248)ATTO 390 (3)ATTO 488 (6)ATTO 550 (1)ATTO 594 (5)ATTO 647N (4)AVI (53)Beads (235)Beta Gal (2)BgG (1)BIMA (6)Biotin (27817)Biotinylated (1810)Blue (708)BSA (878)BTG (46)C Terminal (688)CF Blue (19)Colloidal (22)Conjugated (29281)Cy (163)Cy3 (390)Cy5 (2041)Cy5 5 (2469)Cy5 PE (1)Cy7 (3638)Dual (170)DY549 (3)DY649 (3)Dye (1)DyLight (1430)DyLight 405 (7)DyLight 488 (216)DyLight 549 (17)DyLight 594 (84)DyLight 649 (3)DyLight 650 (35)DyLight 680 (17)DyLight 800 (21)Fam (13)Fc Tag (8)FITC (29181)Flag (208)Fluorescent (146)GFP (576)GFP Tag (180)Glucose Oxidase (59)Gold (511)Green (580)GST (722)GST Tag (327)HA Tag (440)His (634)His Tag (507)Horseradish (550)HRP (12994)HSA (247)iFluor (16571)Isoform b (31)KLH (87)Luciferase (105)Magnetic (260)MBP (343)MBP Tag (93)Myc Tag (410)OC 515 (1)Orange (78)OVA (103)Pacific Blue (213)Particle (64)PE (32633)PerCP (7450)Peroxidase (1364)POD (11)Poly Hrp (94)Poly Hrp40 (13)Poly Hrp80 (3)Puro (32)Red (2440)RFP Tag (63)Rhodamine (607)RPE (910)S Tag (194)SCF (184)SPRD (351)Streptavidin (55)SureLight (77)T7 Tag (97)Tag (4806)Texas (1249)Texas Red (1231)Triple (10)TRITC (1401)TRX tag (90)Unconjugated (2110)Unlabeled (218)Yellow (84)Pathogen (489480)
Adenovirus (8685)AIV (317)Bordetella (25032)Borrelia (18284)Candida (17811)Chikungunya (638)Chlamydia (17663)CMV (121402)Coronavirus (5949)Coxsackie (859)Dengue (2872)EBV (1497)Echovirus (215)Enterovirus (677)Hantavirus (259)HAV (909)HBV (2084)HHV (838)HIV (7876)hMPV (275)HSV (2334)HTLV (635)Influenza (22004)Isolate (1208)KSHV (396)Lentivirus (3755)Lineage (3025)Lysate (127759)Marek (94)Measles (1169)Parainfluenza (1692)Poliovirus (3024)Poxvirus (81)Rabies (1526)Reovirus (536)Retrovirus (1066)Rhinovirus (511)Rotavirus (5353)RSV (1768)Rubella (1070)SIV (279)Strain (67791)Vaccinia (7232)VZV (661)WNV (369)Species (2980604)
Alligator (10)Bovine (159815)Canine (120805)Cat (13115)Chicken (113989)Cod (1)Cow (2031)Dog (12723)Dolphin (21)Duck (9606)Equine (2012)Feline (1019)Ferret (259)Fish (12882)Frog (1)Goat (90541)Guinea Pig (87960)Hamster (36960)Horse (41294)Human (950231)Insect (653)Lemur (119)Lizard (24)Monkey (110994)Mouse (470765)Pig (26229)Porcine (131969)Rabbit (127889)Rat (349272)Ray (443)Salmon (348)Seal (8)Shark (29)Sheep (105155)Snake (11)Swine (519)Toad (4)Turkey (244)Turtle (75)Whale (45)Zebrafish (534)Technique (5589781)
Activation (170412)Activity (10795)Affinity (44634)Agarose (2604)Aggregation (199)Antigen (135460)Apoptosis (27407)Array (2022)Blocking (71768)Blood (8530)Blot (10966)ChiP (814)Chromatin (6286)Colorimetric (9907)Control (80079)Culture (3219)Cytometry (5475)Depletion (56)DNA (172527)Dot (233)EIA (1039)Electron (6275)Electrophoresis (254)Elispot (1294)Enzymes (52765)Exosome (4280)Extract (1090)Fab (2227)FACS (43)FC (80717)Flow (6662)Fluorometric (1406)Formalin (97)Frozen (2671)Functional (708)Gel (2480)HTS (136)IF (12906)IHC (16566)Immunoassay (1589)Immunofluorescence (4119)Immunohistochemistry (72)Immunoprecipitation (68)intracellular (5602)IP (2838)iPSC (259)Isotype (8804)Lateral (1587)Lenti (319416)Light (37303)Microarray (47)MicroRNA (4835)Microscopy (52)miRNA (88042)Monoclonal (524801)Multi (3844)Multiplex (302)Negative (4261)PAGE (2521)Panel (1633)Paraffin (2587)PBS (20266)PCR (9)Peptide (276278)PerCP (12769)Polyclonal (2747043)Positive (6336)Precipitation (61)Premix (130)Primers (3467)Probe (2630)Profile (229)Pure (7818)Purification (15)Purified (78235)Real Time (3042)Resin (2975)Reverse (2438)RIA (460)RNAi (17)Rox (1023)RT PCR (6608)Sample (2666)SDS (1524)Section (2895)Separation (86)Sequencing (122)Shift (22)siRNA (319447)Standard (42465)Sterile (10168)Strip (1863)Taq (2)Tip (1172)Tissue (42847)Tube (3306)Vitro (3577)Vivo (981)WB (2515)Western Blot (10683)Tissue (2017019)
Adenocarcinoma (1075)Adipose (3463)Adrenal (657)Adult (4883)Amniotic (65)Animal (2452)Aorta (436)Appendix (89)Array (2022)Ascites (4737)Bile Duct (20)Bladder (1675)Blood (8530)Bone (27367)Brain (31217)Breast (10918)Calvaria (28)Carcinoma (13497)cDNA (58548)Cell (413914)Cellular (9360)Cerebellum (700)Cervix (232)Child (1)Choroid (19)Colon (3911)Connective (3603)Contaminant (3)Control (80079)Cord (661)Corpus (148)Cortex (698)Dendritic (1849)Diseased (265)Donor (1360)Duct (861)Duodenum (643)Embryo (425)Embryonic (4586)Endometrium (466)Endothelium (1424)Epidermis (166)Epithelium (4224)Esophagus (716)Exosome (4280)Eye (2033)Female (475)Frozen (2671)Gallbladder (155)Genital (5)Gland (3437)Granulocyte (8990)Heart (6851)Hela (413)Hippocampus (325)Histiocytic (74)Ileum (201)Insect (4880)Intestine (1945)Isolate (1208)Jejunum (175)Kidney (8079)Langerhans (283)Leukemia (21573)Liver (17342)Lobe (835)Lung (6074)Lymph (1208)Lymphatic (639)lymphocyte (22589)Lymphoma (12787)Lysate (127759)Lysosome (2814)Macrophage (31832)Male (1617)Malignant (1467)Mammary (1987)Mantle (1042)Marrow (2210)Mastocytoma (3)Matched (11710)Medulla (156)Melanoma (15525)Membrane (105780)Metastatic (3575)Mitochondrial (160331)Muscle (37428)Myeloma (748)Myocardium (11)Nerve (6403)Neuronal (17035)Node (1206)Normal (9488)Omentum (10)Ovarian (2511)Ovary (1173)Pair (47185)Pancreas (2843)Panel (1633)Penis (64)Peripheral (1912)Pharynx (122)Pituitary (5421)Placenta (4051)Prostate (9438)Proximal (318)Rectum (316)Region (202208)Retina (956)Salivary (3119)Sarcoma (6946)Section (2895)Serum (24921)Set (167648)Skeletal (13636)Skin (1882)Smooth (7575)Spinal (424)Spleen (2292)Stem (8901)Stomach (925)Stroma (49)Subcutaneous (47)Testis (15396)Thalamus (127)Thoracic (60)Throat (40)Thymus (2988)Thyroid (14138)Tongue (144)Total (10151)Trachea (227)Transformed (175)Tubule (48)Tumor (76992)Umbilical (208)Ureter (73)Urinary (2467)Uterine (303)Uterus (414)Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Sequencing (ChIP-seq)
“Comprehensive ChIP-seq guide explaining genome-wide protein-DNA interactions, chromatin profiling, histone marks, and advanced NGS analysis for scientific education.”
Gentaur
Scientific Publications

Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Sequencing (ChIP-seq)
Introduction to ChIP-seq
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Sequencing universally known as ChIP-seq is one of the most influential techniques in modern genomics.
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Sequencing (ChIP-seq) is a genome-wide method used to identify protein-DNA binding events, histone modifications, and chromatin-associated regulatory mechanisms with high accuracy.
Combining immunoprecipitation with next-generation sequencing (NGS), ChIP-seq offers a precise, scalable approach for mapping epigenomic landscapes.
What Makes ChIP-seq Important ?
ChIP-seq enables researchers to uncover where specific proteins bind on DNA, including:
- Transcription factors
- Histone modifications
- Chromatin-associated proteins
- Epigenetic regulators
Genome-wide protein occupancy patterns
By revealing these interaction sites, ChIP-seq helps scientists understand gene regulation, chromatin architecture, and cellular identity on a genomic scale. NCBI
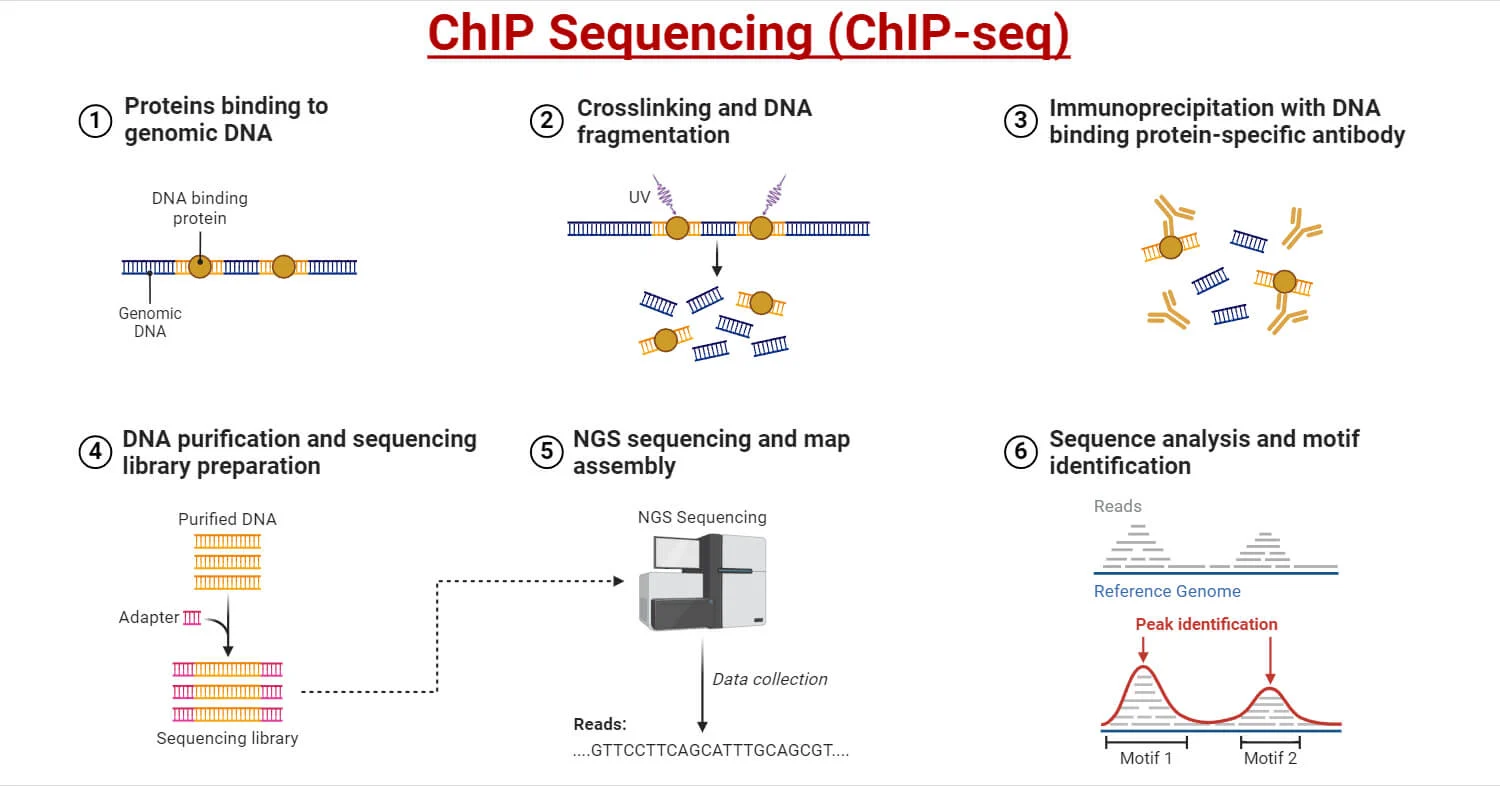
The ChIP-seq Workflow
ChIP-seq relies on a multi-stage experimental design integrating molecular preparation, immunoprecipitation, sequencing library generation, and computational analysis.
1-Crosslinking of Protein-DNA Complexes
Crosslinking stabilizes protein–DNA interactions in vivo.
Formaldehyde is commonly used due to its reversible nature and short crosslink distances. Advanced protocols may use :
- Formaldehyde alone (most common).
- Dual crosslinking (e.g., DSG + formaldehyde).
- UV-crosslinking for nucleic acid–protein complexes.
2-Chromatin Extraction and Fragmentation
Once crosslinked, cells undergo lysis and chromatin extraction.
Two primary fragmentation strategies exist :
Mechanical Fragmentation
- Sonication using focused ultrasonication instruments
- Generates fragments between 100 – 600 bp
- Ideal for transcription factor ChIP-seq
Enzymatic Digestion
- Micrococcal nuclease (MNase)
- Produces nucleosome-sized fragments
- Preferred for histone modification studies
3-Immunoprecipitation Using Highly Specific Antibodies
The immunoprecipitation step enriches DNA fragments bound to the protein of interest.
Key variables include :
- Antibody specificity
- Epitope affinity
- Batch consistency
- Chromatin input quality
Magnetic beads coated with Protein A/G are commonly used.
4-Reverse Crosslinking and DNA Purification
After immunoprecipitation, the following steps occur :
- Reverse crosslinking (typically at high temperature)
- Protease treatment
- Purification of ChIP-DNA
This yields high-enrichment, low-background DNA suitable for sequencing.
Library Preparation for Next-Generation Sequencing
Library construction involves :
- End repair
- A-tail addition
- Adapter ligation
- PCR amplification
- Size selection
Bioinformatics Analysis
Read Quality Control (QC)
Standard QC involves :
-Phred score evaluation
-Adapter trimming
-Removal of low-quality reads
Alignment to Reference Genome
Reads are mapped to reference genomes using high-performance aligners :
-BWA-MEM
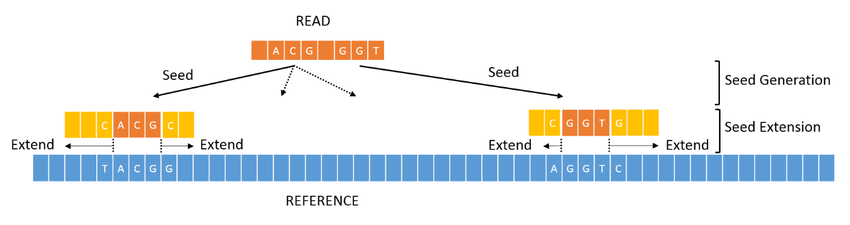
-Bowtie2

-HISAT2

Peak Calling : Identifying Protein Binding or Histone Mark Enrichment
Peak calling is a cornerstone of ChIP-seq analysis.
Tools include :
-MACS2 (Model-based Analysis of ChIP-seq). NCBI

-SICER (useful for broad histone marks)
-HOMER
Normalization and Control Correction
Input DNA or IgG controls allow removal of sequencing bias.
Normalization strategies include :
-RPM (Reads Per Million)
-RPKM
-Spike-in normalization
-Background subtraction
Motif Discovery and Functional Annotation
Once peaks are identified, downstream analysis includes :
-Motif enrichment analysis
-Gene ontology (GO) enrichment
-Pathway association analysis
-Peak annotation to promoters, enhancers, or intergenic regions
These steps bridge ChIP-seq data with functional genomic interpretation.
Applications of ChIP-seq
Transcription Factor Binding Maps
Transcription factors modulate gene expression.
ChIP-seq identifies :
- motif preferences
- co-factor interactions
- regulatory networks
- genomic occupancy patterns.
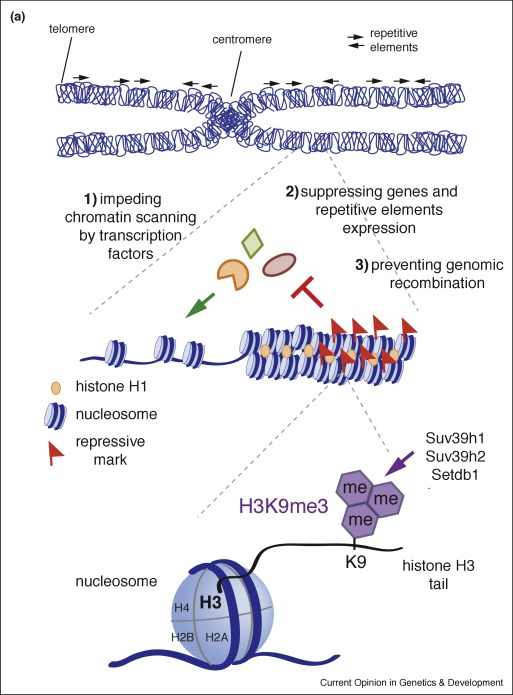
Histone Modification Profiling
Different histone marks correspond to specific regulatory states :
-H3K4me1 : enhancers

-H3K4me3 : active promoters

-H3K27ac : active regulatory regions

-H3K27me3 : repressed chromatin

-H3K9me3 : heterochromatin
Chromatin State Dynamics
When combined with :
-ATAC-seq

-RNA-seq

-Hi-C

-DNA methylation assays

Comparative Genomics
Comparisons across species, conditions, or development stages provide insights into :
- evolutionary conservation
- epigenomic divergence
- environmental adaptation
Strengths and Limitations of ChIP-seq
Strengths
- High resolution
- Genome-wide scope
- Compatibility with many proteins
- Strongly supported by bioinformatics tools
- Generates interpretable peak landscapes
Limitations
- Dependent on antibody quality
- Requires significant sequencing depth
- Computationally intensive
- May generate false positives without proper controls
Tags
- ChIP-seq
- Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Sequencing
- Generation sequencing
- Epigenomics
- Protein-DNA interactions
- Transcription factors
- Chromatin profiling
- NGS Workflow
- Bioinformatics Analysis
